- Topics
- News
- Blogs
- Podcasts
- Buyers Guide
- Magazine
- Advertise
Infectious Disease
Weekly Digest: HPAI financial assistance and testing updates for dairies
FARM Program releases new versions, and $12 million in grant funding announced for dairy initiatives.
Read More
Third dairy farmworker diagnosed with H5N1; more herd status testing options available
The USDA received an additional $824 million in emergency funding and announced a pilot program to offer bulk milk testing prior to interstate animal movement.
Read More
Dairy herd in Colorado tests positive for HPAI
Mandatory testing for interstate cattle movement begins today.
Read More
USDA mandates influenza A testing for interstate movement of dairy cattle
Effective April 29, these mandates for testing and reporting of results are intended to further protect livestock from the threat of HPAI.
Read More
Implementing an autogenous vaccine for pinkeye: It’s so easy, even an academic vet can do it
Pinkeye development, treatment and prevention, and how to create and implement an autogenous vaccine.
Read More
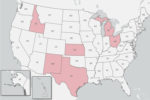
HPAI confirmed in dairy cattle in eight states, some states restricting cattle movement
North Carolina and South Dakota are now among states with confirmed cases of HPAI. At least 18 states have placed restrictions on the movement of cattle.
Read More
Avian influenza cases confirmed on Idaho, New Mexico, Ohio dairies and one human
The strain of the virus in all herds remains similar to the first detected, and risk to public health remains low.
Read More